Discover the vital role of iron as an essential mineral for oxygen transport, wound healing, and growth.
What is Iron?
Iron is an essential mineral that, according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), many Americans do not get enough of. This is why it is a mandatory nutrient to be listed on all nutrition facts panels you see on the back of a food product’s packaging. Iron plays a variety of critical roles, including carrying oxygen in your blood, facilitating wound healing, and supporting normal growth and development.1
RDA’s and Sources
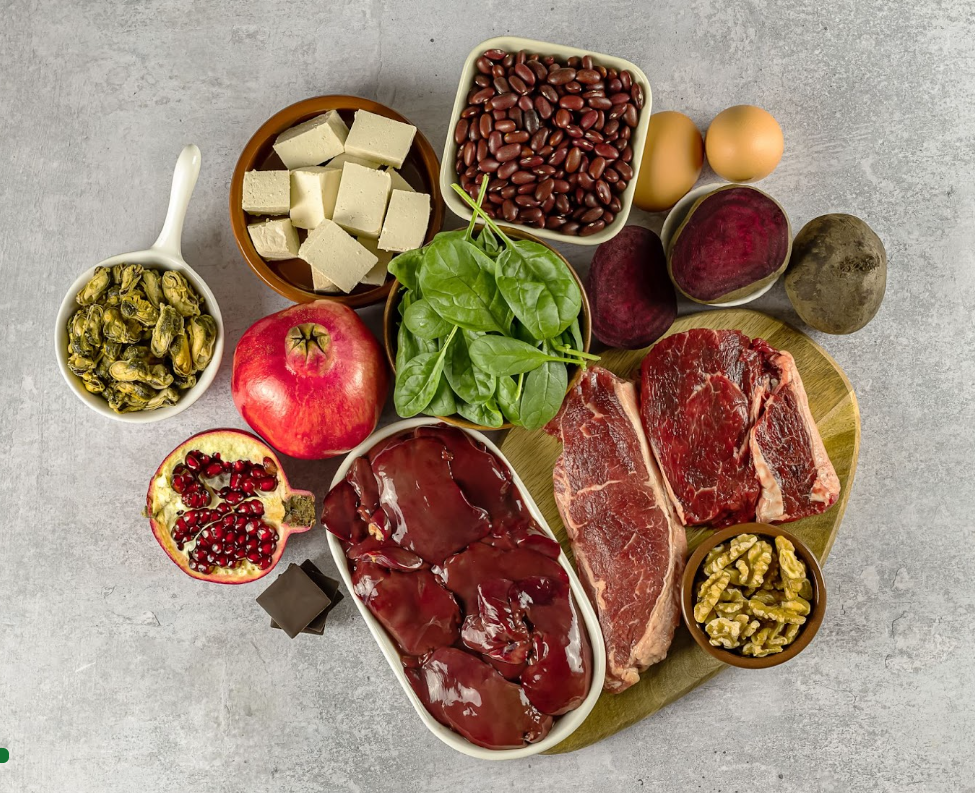
It’s essential to ensure you get enough iron each day, especially for women and those following a plant-based or vegan diet. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), the Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for iron for males aged 19-50 years is 8 mg per day, and females aged 19-50 years need more than double that amount at about 18 mg per day. Pregnant women aged 14-50 years need about 27 mg of iron per day and 10 mg a day during lactation.3 Common sources of iron include red meats, organ meats, poultry, seafood, eggs, beans, nuts and seeds, and fortified foods like cereals or iron supplements.
Relationship Between Vitamin C and Iron
Did you know that certain foods can increase the absorption of iron when eaten within the same meal? Foods with vitamin C, when paired with iron, work to increase absorption of dietary iron by changing it to a more absorbable form of iron, called ferrous iron. Examples of this pairing could be broccoli and steak, tomato sauce and fortified pasta, beans and bell peppers, or fortified cereal and strawberries.
Types of Iron
There are two types of iron found in the foods we eat, heme iron and non-heme iron. Heme iron is found primarily in animal sources like red meat, poultry, fish, and seafood, and is more easily absorbed on its own compared to non-heme iron. Non-heme iron sources are plant-based, like beans, spinach, tofu, and fortified foods. Since non-heme iron sources aren't as easily absorbed on their own, it may be a good idea to incorporate foods with vitamin C when having meals containing plant-based iron.2
*This information is intended for general educational purposes only and does not constitute individual medical or nutrition advice. Please consult your physician or registered dietitian for personalized recommendations based on your specific health needs.
Sources
Cleveland Clinic. Should You Take Iron with Vitamin C? Cleveland Clinic. Published December 8, 2023. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/iron-and-vitamin-c
American Red Cross. Iron-Rich Foods. Redcrossblood.org. Published 2019. https://www.redcrossblood.org/donate-blood/blood-donation-process/before-during-after/iron-blood-donation/iron-rich-foods.html
National Institutes of Health. Office of Dietary Supplements - Iron. Nih.gov. Published 2017. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/#h2